ISLAMABAD: The third budget of the PTI government, announced on Friday, aims to reduce the input cost of several industries. It also plans on tapping online transactions and bring these under the Sales Tax (ST) net.
The Budget 2021-22 offers unprecedented relief measures in Customs Duty (CD), ST and Income Tax (IT) for the industrial sector amid a proposed plan that explains how the government intends to meet the Rs1,129 billion hike in the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) target.
As per proposed plan, under the revenue relief changes announced in the Finance Bill, the government aims to give away Rs119bn to industries and individuals. Of these, Rs42bn has been given in CD, 19bn in ST and Federal Excise Duty (FED) while Rs58bn in IT.
The revenue measures under IT will generate Rs116bn, followed by Rs215bn from ST & FED and Rs53bn from CD measures. The net revenue impact will be Rs264bn after deduction of relief measures.
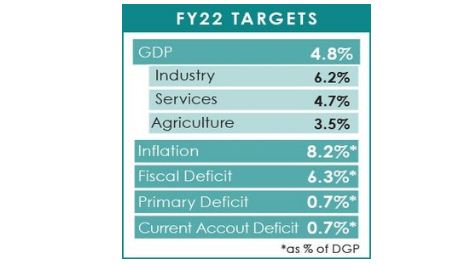
Official documents suggest that GDP growth at the rate of 5.2pc in FY22 will help generate Rs236bn while projected inflation at 8.2pc will yield an additional revenue of Rs385bn. The FBR aims to collect an additional revenue of Rs242bn from enforcement.
The cumulative impact of all these measures will be Rs1,127bn to reach the target of Rs5.829tr for FY22.
Additional revenue measures to raise Rs383bn
FED has been proposed on potassium chlorate, reclaimed lead and electronically-heated tobacco products. The government proposed withdrawing FED on industrial units located in the erstwhile FATA/PATA. FED has been reduced to 16pc from 17pc on telecommunication to facilitate business and provide relief to masses.
On the intervention of Prime Minister Imran Khan the proposed FED on usage of mobile and internet, which earlier in the cabinet meeting approved was reversed through a tweet late night. FBR estimates show Rs100bn from this levy.
Locally-manufactured small cars up to engine capacity of 850cc are exempted from excise duty along with reduction in ST rate from 17pc to 12.5pc and withdrawal of value-added tax.
Industrial relief measures
The government has either reduced or exempted completely CD, additional customs duty (ACD) and Regulatory Duty (RD) on imports of 584 tariff lines including fabric in the value chain of the textile sector. The estimated loss of revenue from this major measure is Rs10bn
It was proposed to rationalise CD, ACD and RD on the import of flat-rolled products of HRC and stainless steel.
Tariff policy board has proposed reduction in CD and ACD on 328 tariff lines related to raw materials, chemicals and intermediate goods for chemical, engineering and leather industry, etc as part of its tariff rationalisation plan. Under this, 241 tariff lines are completely exempted from CD and ACD while CD and ACD on 87 tariff lines reduced to 3pc from 16pc, 11pc.
To incentivise pharmaceutical products, CD and ACD has been exempted on 358 active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), raw material of auto-disable syringes and Remdesivir.
CD reduced from 20pc to 16pc and ACD from 7pc to 4pc on uncoated paper and paperboard for printing and graphic arts industry; exemption on raw materials for vaccines and feed additives to incentivise the dairy sector. CD reduced 50pc duty on 100 tariff lines relating to adventure tourism. The government reduced duty to 3pc from 11pc on inputs for poultry industry.
On 2,436 tariff lines, ACD has been reduced from 7pc to 6pc. These items are placed under the 20pc CD slab. This slab includes garments, footwear, processed food, home appliances and other goods.
Regulatory duty
It has been proposed to impose Rs15,000 as RD on import of high-end mobiles. However, the prime minister has not approved the measure. The revenue impact of this measure is calculated at Rs16bn.
The rates of RD have been further scaled up on 78 tariff lines on import of non-essential/luxury items to support local industry. This will increase revenue collection by over Rs11bn. The net effect of tariff rationalisation for the auto sector is Rs15bn.
The increase in RD rate on import of tyres by 5pc to 10pc will generate Rs5bn. The government imposed 10pc RD on import of uncoated paper, paper board, neutral glass tubing and pencils and crayons.
The government levied 17pc sales tax on crude oil and other items by withdrawing zero rating. This levy will generate Rs38bn for the government. A 17pc GST imposed on 42 imported food items including like cereals, milk and cream, frozen meat and sausages, fat filled milk at. This will lead to a revenue collection of Rs14bn.
A 17pc sales tax imposed on several products like silver, gold jewelry, fat filled milk, LNG/RLNG to raise Rs35bn for the FBR. FBR will collect Rs11bn from e-commerce and Rs7bn on collection of sales tax on sugar at retail sector and another 8bn from integrated POS retailers.
Income tax
The government has proposed Rs51bn worth new income tax measures in the budget. The Rs65bn worth exemptions and concessions withdrawn through an ordinance have now made part of the Finance Bill. Twelve withholding taxes were withdrawn- on banking transactions, air travel, stock exchange, CNG, petroleum products, international debit credit card transactions, and extraction of minerals.
It has proposed to introduce normal tax by eliminating block taxation of property income, capital gains and rental incomes. The government aims to generate Rs10bn from all these three measures.
The export proceeds of services, to be taxed at 1pc, and another Rs20 bn from streamlining procedures and automation of business process for monitoring of withholding tax.
It proposed to levy 7.5pc withholding tax on domestic electricity bill above Rs25,000 per month. However, no tax will be charged in case of existing on taxpayers list. Minimum tax rates reduced from 1.5pc to 1.25pc for all person, 0.75pc to 0.5pc refineries, 1.25pc to 0.25pc fast moving goods sold by retailers and exempted for SEZ/TEZ.