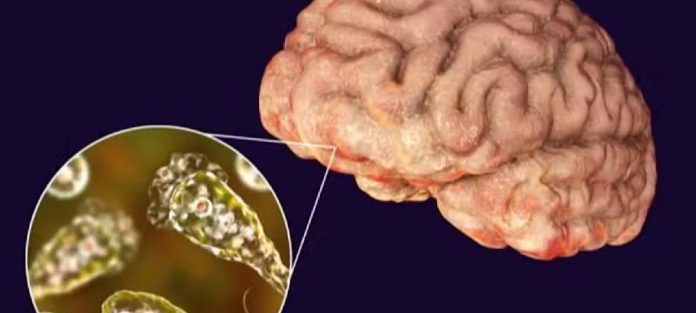
The National Institute of Health (NIH) has issued an advisory concerning Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM), also known as Naegleriasis or brain-eating amoeba, a serious infectious disease affecting the central nervous system.
Since 2008, deaths related to PAM have been reported in some Karachi hospitals during the summer months. The advisory highlights that high temperatures combined with poorly chlorinated water during early summer increase the risk of Naegleria fowleri infection.
The advisory aims to alert public health authorities, water and sanitation agencies, and other relevant stakeholders to take necessary actions to prevent and control PAM, particularly in areas with annual cases.
Naegleria fowleri cannot survive in clean, cool, and chlorinated water, as chlorine is the most effective way to disinfect swimming pools and water systems.
People have been advised to avoid jumping or diving into warm freshwater or thermal pools and to keep their heads above water in spas, thermal pools, and warm fresh water. Small collapsible wading pools should be emptied and cleaned daily.
Swimming pools and spas should be adequately chlorinated and well maintained. When using un-chlorinated water, individuals should avoid letting water enter their noses during bathing, showering, or washing their faces.